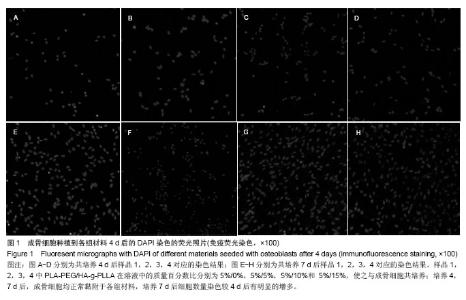
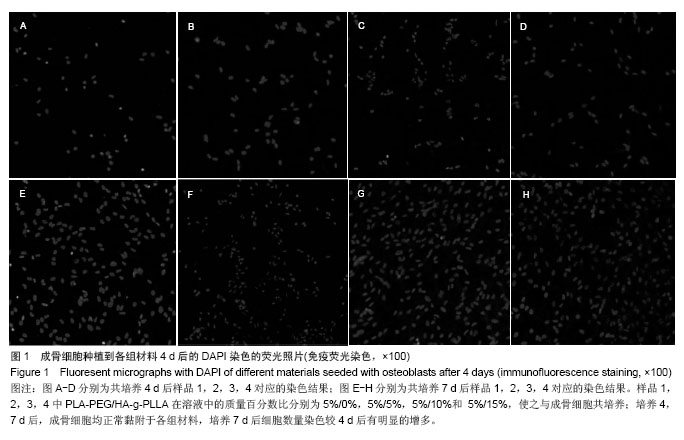
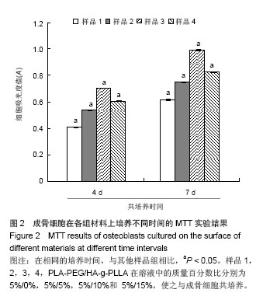
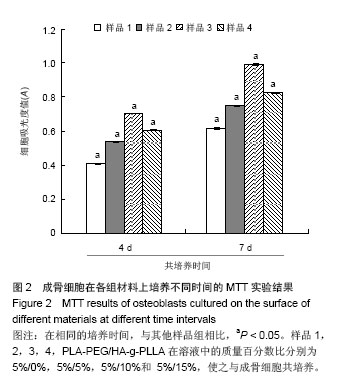
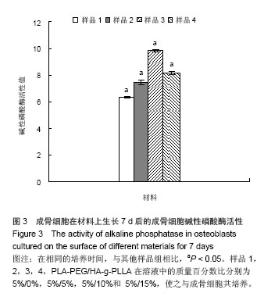
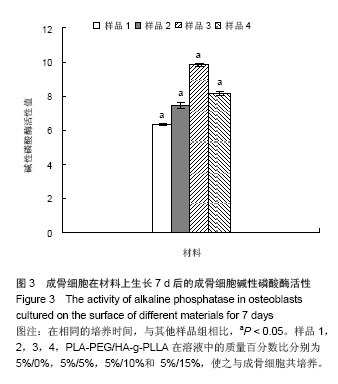
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (39): 6246-6251.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.39.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of polylactic acid-polyethylene glycol composite fibrous materials on adhesion, multiplication and viability of osteoblasts
Lu Jian1, Yang Zhen-lei2, Hou Ren3
- 1 Department of Spine Surgery, 3Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University, Guilin 541000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2 Department of Orthopedics, Heze Municipal Hospital, Heze 274000, Shandong Province, China
-
Online:2014-09-17Published:2014-09-17 -
Contact:Lu Jian, Department of Spine Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University, Guilin 541000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Lu Jian, M.D., Department of Spine Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University, Guilin 541000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lu Jian, Yang Zhen-lei, Hou Ren. Effect of polylactic acid-polyethylene glycol composite fibrous materials on adhesion, multiplication and viability of osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(39): 6246-6251.
share this article
| [1]Morishita T, Honoki K, Ohgushi H, et al. Tissue engineering approach to the treatment of bone tumors: three cases of cultured bone grafts derived from patients' mesenchymal stem cells. Artif Organs. 2006;30(2):115-118.
[2]Zhang D, Chang J, Zeng Y. Fabrication of fibrous poly(butylene succinate)/wollastonite/apatite composite scaffolds by electrospinning and biomimetic process. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19(1):443-449.
[3]杨振磊,卢剑,蒋尧传.骨组织工程高分子材料和复合材料的研究进展[J].临床医学工程,2013,(11):1460-1461.
[4]丰强,闵思佳,张海萍,等.羟基磷灰石及其复合材料在骨组织工程中的研究进展[J].蚕桑通报,2008(1):9-12.
[5]Mikos AG, Lyman MD, Freed LE, et al. Wetting of poly(L-lactic acid) and poly(DL-lactic-co-glycolic acid) foams for tissue culture. Biomaterials. 1994;15(1):55-58.
[6]Kim P, Kim D H, Kim B, et al. Fabrication of nanostructures of polyethylene glycol for applications to protein adsorption and cell adhesion. Nanotechnology. 2005; 16(10): 2420-2426.
[7]Caliceti P, Salmaso S, Elvassore N, et al. Effective protein release from PEG/PLA nano-particles produced by compressed gas anti-solvent precipitation techniques. J Control Release. 2004;94(1):195-205.
[8]陈佑宁,樊国栋,杨小玲.生物降解材料聚乳酸-聚乙二醇的合成及表征[J].科技导报,2009(13):50-53.
[9]林丽丽,宿烽.PLA-PEG对斑马鱼补体免疫系统的影响[J].青岛科技大学学报(自然科学版),2012,(6):593-598.
[10]Hyon SH, Jamshidi K, Ikada Y. Synthesis of polylactides with different molecular weights. Biomaterials. 1997;18(22): 1503-1508.
[11]彭维海.新型可吸收材料PLLA/PLLA-gHA的生物降解性及生物力学性能的实验研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2009.
[12]Andriano KP, Daniels AU, Heller J. Biocompatibility and mechanical properties of a totally absorbable composite material for orthopaedic fixation devices. J Appl Biomater. 1992;3(3):197-206.
[13]Ma PX. Biomimetic materials for tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60(2):184-198.
[14]Chen J, Yu Q, Zhang G, et al. Preparation and biocompatibility of nanohybrid scaffolds by in situ homogeneous formation of nano hydroxyapatite from biopolymer polyelectrolyte complex for bone repair applications. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2012;93:100-107.
[15]廖世波,赖琛,张志雄,等.骨修复复合材料及其相关问题的研究进展[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2012,(5):755-761.
[16]Damien CJ, Parsons JR. Bone graft and bone graft substitutes: a review of current technology and applications. J Appl Biomater. 1991;2(3):187-208.
[17]Agrawal CM, Best J, Heckman JD, et al. Protein release kinetics of a biodegradable implant for fracture non-unions. Biomaterials. 1995;16(16):1255-1260.
[18]Ben-Shabat S, Kumar N, Domb AJ. PEG-PLA block copolymer as potential drug carrier: preparation and characterization. Macromol Biosci. 2006;6(12):1019-1025.
[19]宋晓峰,凌风光,陈学思.纳米羟基磷灰石表面接枝聚合左旋丙交酯[J].高分子学报,2013,(1):95-101.
[20]Haider A, Gupta K C, Kang IK. PLGA/nHA hybrid nanofiber scaffold as a nanocargo carrier of insulin for accelerating bone tissue regeneration. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2014;9(1):314.
[21]Persson M, Lorite GS, Cho SW, et al. Melt spinning of poly(lactic acid) and hydroxyapatite composite fibers: influence of the filler content on the fiber properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(15):6864-6872.
[22]Elgendy HM, Norman ME, Keaton AR, et al. Osteoblast-like cell (MC3T3-E1) proliferation on bioerodible polymers: an approach towards the development of a bone-bioerodible polymer composite material. Biomaterials. 1993;14(4): 263-269.
[23]邵英.聚L-乳酸/聚L-乳酸接枝的纳米羟基磷灰石复合材料(PLLA/PLLA-gHA)的生物相容性研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2007.
[24]Bansal V, Kumar M, Dalela M, et al. Evaluation of synergistic effect of biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles and aluminum based adjuvant for improving vaccine efficacy. Int J Pharm. 2014;471(1-2):377-384.
[25]Zhan C, Gu B, Xie C, et al. Cyclic RGD conjugated poly(ethylene glycol)-co-poly(lactic acid) micelle enhances paclitaxel anti-glioblastoma effect. J Control Release. 2010; 143(1):136-142.
[26]Cecen B, Kozaci D, Yuksel M, et al. Biocompatibility of MG-63 cells on collagen, poly-L-lactic acid, hydroxyapatite scaffolds with different parameters. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2014.
[27]Sui G, Yang X, Mei F, et al. Poly-L-lactic acid/hydroxyapatite hybrid membrane for bone tissue regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007;82(2):445-454.
[28]Deng X L, Sui G, Zhao M L, et al. Poly(L-lactic acid)/hydroxyapatite hybrid nanofibrous scaffolds prepared by electrospinning. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2007;18(1): 117-130.
[29]Zong C, Qian X, Tang Z, et al. Biocompatibility and bone-repairing effects: comparison between porous poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid and nano-hydroxyapatite/poly (lactic acid) scaffolds. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014;10(6): 1091-1104.
[30]Kim HW, Lee HH, Knowles JC. Electrospinning biomedical nanocomposite fibers of hydroxyapatite/poly (lactic acid) for bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006;79(3): 643-649.
[31]Zhang P, Hong Z, Yu T, et al. In vivo mineralization and osteogenesis of nanocomposite scaffold of poly (lactide-co-glycolide) and hydroxyapatite surface-grafted with poly(L-lactide). Biomaterials. 2009;30(1):58-70.
[32]Busa W B, Nuccitelli R. Metabolic regulation via intracellular pH. Am J Physiol. 1984;246(4 Pt 2):R409-R438.
[33]Lu HH, Tang A, Oh S C, et al. Compositional effects on the formation of a calcium phosphate layer and the response of osteoblast-like cells on polymer-bioactive glass composites. Biomaterials. 2005,26(32):6323-6334.
[34]Persson M, Lorite GS, Kokkonen HE, et al. Effect of bioactive extruded PLA/HA composite films on focal adhesion formation of preosteoblastic cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014; 121:409-416.
[35]Minton J, Janney C, Akbarzadeh R, et al. Solvent-free polymer/bioceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: fabrication, analysis, and cell growth. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2014:1-19.
[36]Lugovskoy A, Lugovskoy S. Production of hydroxyapatite layers on the plasma electrolytically oxidized surface of titanium alloys. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;43C: 527-532.
[37]Alothman OY, Fouad H, Al-Zahrani SM, et al. Thermal, creep-recovery and viscoelastic behavior of high density polyethylene/hydroxyapatite nano particles for bone substitutes: effects of gamma radiation. Biomed Eng Online. 2014;13:125.
[38]Teepe JD, Schmitz JE, Hu Y, et al. Correlation of ameloblastin with enamel mineral content. Connect Tissue Res. 2014;55 Suppl 1:38-42.
[39]Lopas LA, Belkin NS, Mutyaba PL, et al. Fractures in Geriatric Mice Show Decreased Callus Expansion and Bone Volume. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 .
[40]Guerder PY, Deymier-Black AC, Swinteck NZ, et al. Multi-phonon scattering processes in one-dimensional anharmonic biological superlattices: understanding the dissipation of mechanical waves in mineralized tissues. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2014;37:24-32.
[41]Orzechowska S, Wróbel A, Goncerz G, et al. Physicochemical and micro-tomographic characterization of inorganic deposits associated with aortic stenosis. J Heart Valve Dis. 2014;23(1): 40-47.
[42]Yatongchai C, Wren AW, Curran DJ, et al. Investigating the effect of SiO2-TiO2-CaO-Na2O-ZnO bioactive glass doped hydroxyapatite: characterisation and structural evaluation. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(7):1645-1659.
[43]Gunduz O, Gode C, Ahmad Z, et al. Preparation and evaluation of cerium oxide-bovine hydroxyapatite composites for biomedical engineering applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2014;35:70-76.
[44]Kim DY, Han YH, Lee JH, et al. Characterization of multiwalled carbon nanotube-reinforced hydroxyapatite composites consolidated by spark plasma sintering. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:768254.
[45]Yang XB, Webb D, Blaker J, et al. Evaluation of human bone marrow stromal cell growth on biodegradable polymer/ bioglass composites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006; 342(4):1098-1107. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [3] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [4] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [5] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [6] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [7] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [8] | Wang Yujiao, Liu Dan, Sun Song, Sun Yong. Biphasic calcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet rich fibrin can promote the activity of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| [9] | Zhou Jihui, Yao Meng, Wang Yansong, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Influence of novel nanoscaffolds on biological behaviors of neural stem cells and the related gene expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 532-536. |
| [10] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [11] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [12] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [13] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [14] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [15] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||